
A healthy tooth.
To understand root canal treatments, it’s important to know a little about tooth anatomy. The portion of the tooth that you can see above the gum line is called the crown of the tooth. The rest of the tooth is anchored in the bone and is called the root. The number of roots ranges from one to three. Every living tooth has a nerve and a blood supply that comes in through the tip of the root and occupies a space in the middle of each root called the root canal and then fills up a space in the innermost part of the crown of the tooth called a pulp chamber. This living nerve and blood supply area can become infected and, in some cases, causes severe pain. The following is a more detailed explanation from the Canadian Dental Association website:
A healthy tooth.
When bacteria (germs) enter your tooth through deep cavities, cracks or flawed fillings, your tooth can become abscessed. An abscessed tooth is a tooth with an infection in the pulp. If pulp becomes infected, it needs to be removed. An abscessed tooth may cause pain and/or swelling. Your dentist may notice the infection from a dental x-ray or from other changes with the tooth. If left untreated, an abscessed tooth can cause serious oral health problems.
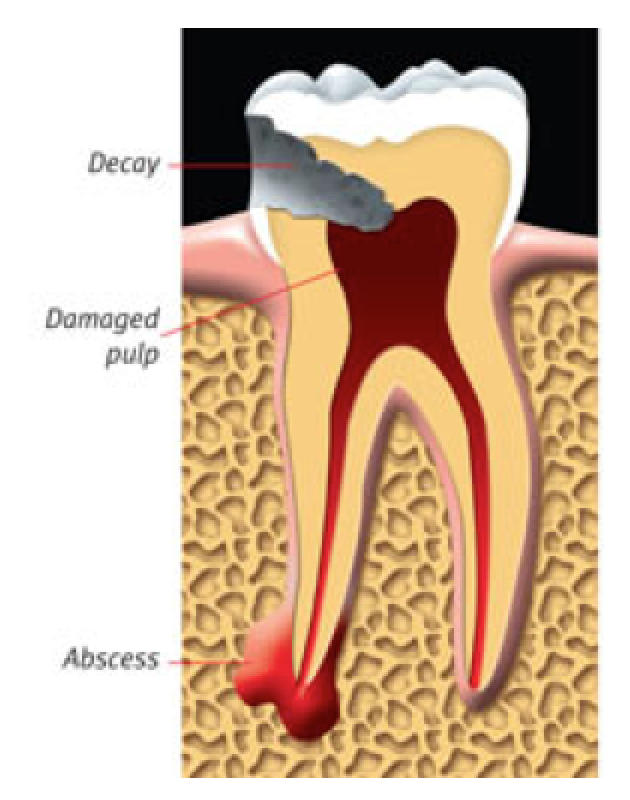
An abscessed tooth.
Who does this procedure?
Your dentist may do root canal treatment or refer you to an endodontist. An endodontist is a dentist who has completed a university post-graduate specialty program in endodontics. Endodontics is a specialty of dentistry concerned with the treatment of the dental pulp or nerve of the tooth.
If your child’s primary (baby) tooth is damaged, your dentist may refer you to a pediatric dentist for this procedure. A pediatric dentist has at least 2 years of extra university training in treating children.
How is a root canal treatment done?
The dentist gives you a local anesthetic (freezing).
To protect your tooth from bacteria in your saliva during the treatment, the dentist places a rubber dam around the tooth being treated.
The dentist makes an opening in the tooth to reach the root canal system and the damaged pulp.
Using very fine dental instruments, the dentist removes the pulp by cleaning and enlarging the root canal system.
After the canal has been cleaned, the dentist fills and seals the canal.
The opening of the tooth is then sealed with either a temporary or permanent filling.
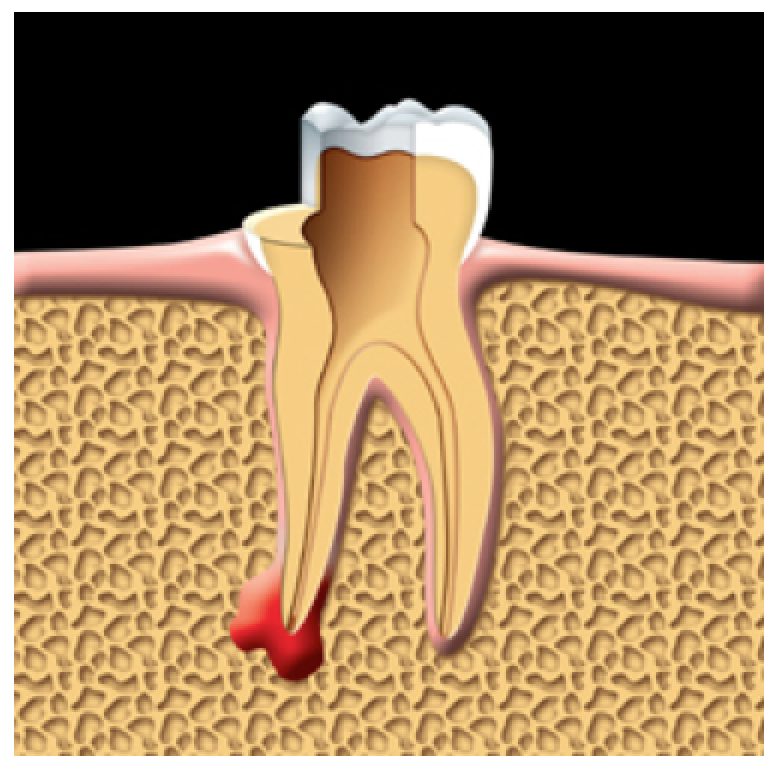
The damaged pulp is removed.
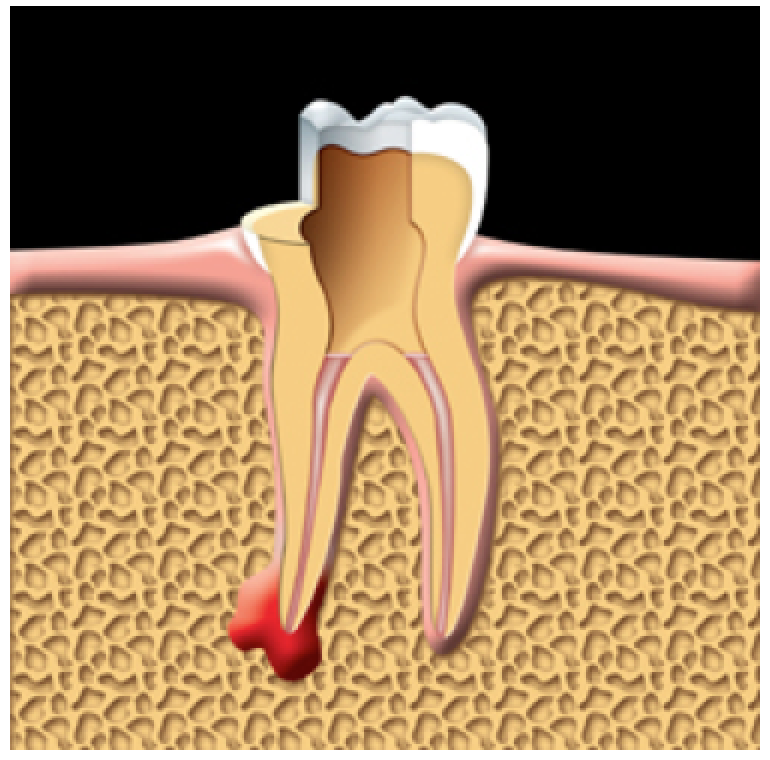
The root canals are filled and sealed.
Tooth restoration after root canal treatment
After a root canal treatment, your tooth has to be restored (fixed) to look, feel and work as much like a natural tooth as possible. If an endodontist performed your root canal treatment, he or she will fill the opening of the tooth with a temporary filling and send you back to your dentist or prosthodontist for tooth restoration.
A prosthodontist is a dental specialist who restores and replaces teeth using crowns, bridges, dentures and implants. Your dentist or specialist may use a permanent filling or a crown to restore your tooth. The choice of restoration will depend on the strength of the part of the tooth that’s left. A back tooth will likely need a crown because chewing puts a great deal of force on back teeth. If there is not enough of the tooth left, posts may be used to help support the crown.
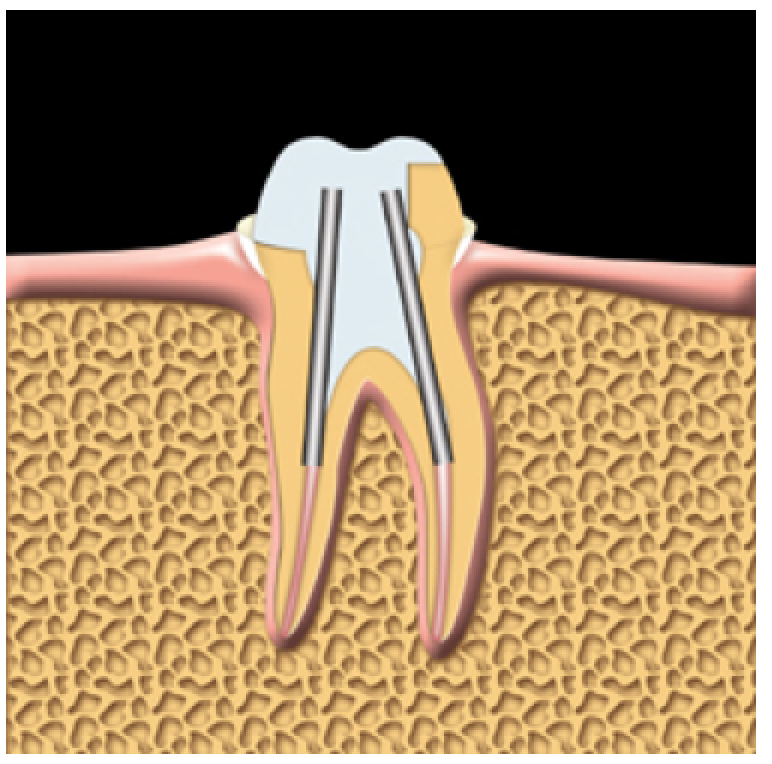
The tooth is prepared for a crown. Posts are used to help support the crown.
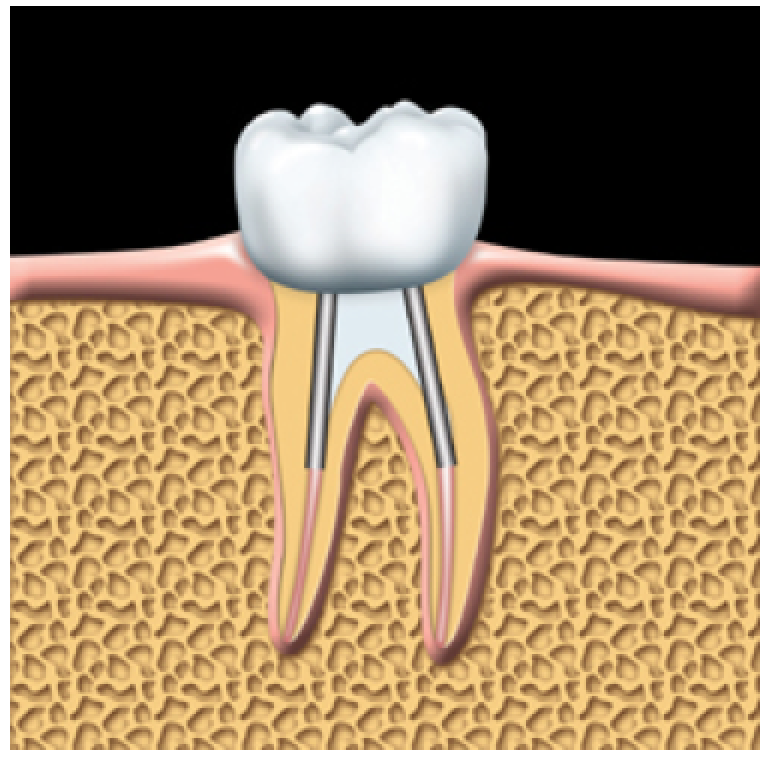
The crown is cemented into place.
What else should I know?
Root canal treatment may be done in 1 or 2 appointments. After root canal treatment, your tooth may be tender for the first week or two. Bad pain or swelling are NOT common. If this happens, call your dentist or endodontist.
You can still get a cavity or gum disease after a root canal treatment. Root canal treatment does not protect your tooth from other types of damage. With proper care and regular dental visits, the tooth could last as long as your other teeth. Most of the time, a tooth that has had a root canal treatment can be saved. However, there are cases where everything possible has been done to save a tooth and still the tooth must be extracted (pulled).
Root canal retreatment
Most root canal treatments are successful. But in some rare cases, a second root canal treatment is needed. This is called retreatment. When retreating a tooth, the root canal filling material is taken out, and the canal is recleaned, reshaped and refilled.
Root canal surgery
Sometimes root canal surgery is needed when a regular root canal treatment cannot be done or when it has not worked. Surgery is done to:
Check the end of the root for fractures (cracks).
Remove parts of the root that could not be cleaned during regular root canal treatment.
Clear up an infection that did not heal after regular treatment.
